Case Study:
Transfection & Vaccines.
What was the challenge?
Internalisation of compounds, proteins or peptides in cells is an important method in immunologic studies. This may be relevant to studies on vaccine or drug development that require transfer of product into a target cell for expression of the product and/or activation of the cell for an immune response. The delivery of products may be carried out by carriers such as nanoparticles or viral vectors, or via active internalisation of the cell, or through cell transfection reagents.
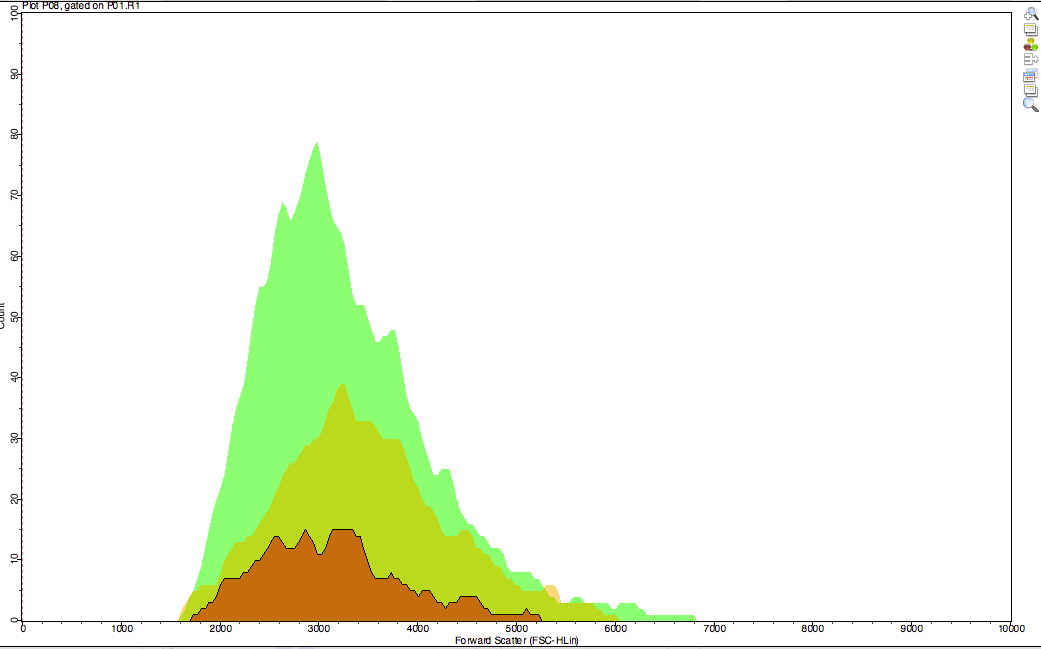
| Description | R8 % | R8 MFI | |
|
Dotted line |
Dendritic cells (only) | 0.0 | 83 |
| Orange filled |
Dendritic cells + load (non-fluorescent) |
2.3 | 89 |
|
Grey filled |
Dendritic cells + load (negative control) |
2.5 | 69 |
|
Green filled |
Dendritic cells + load (fluorescent) |
69 | 1120 |
Problem:
Studying vaccine or drug development that require transfer of product into a target cell for expression of the product and/or activation of the cell for an immune response.
Approach:
We adopted a cell line based dendritic cell (DC) model to transfer mRNA carried by a nanoparticle carrier. Both fluorescent and non-fluorescent protein products (load) were transferred as mRNA to assess translation and availability of proteins in DCs by flow cytometry.
Findings:
There was a high availability of the fluorescent protein in the DCs.
Additional value:
This model can be used in various efficacy testing such as
- Intracellular inhibitors that impact cell signalling and gene expression
- New vaccines (protein or mRNA) in dendritic cell adaptive immunity
- Drug availability in cells