Case Study:
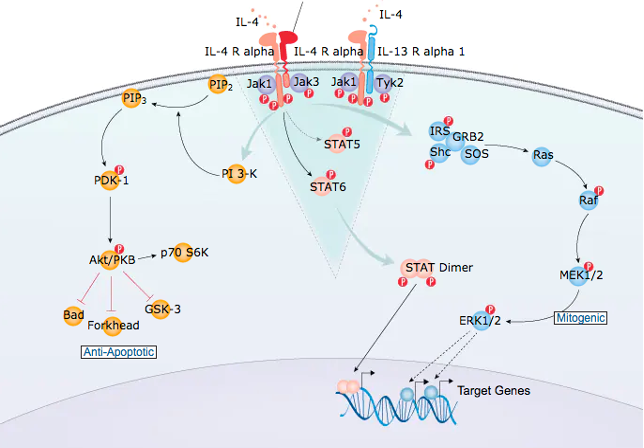
Signalling Pathways.
What was the challenge?
The immune system is very complex consisting of various immune cells of myeloid, lymphoid and other origins. The study of an immune response in understanding the efficacy or risk of a compound can involve complex signalling pathways of multiple cell types, receptors and/or cytokines/growth factors with the outcome of readouts that may not be interpreted through standard or single assays. Such studies require knowledge in signalling pathways and additional tests and methods to generate data to get a better meaning.
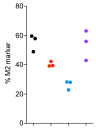
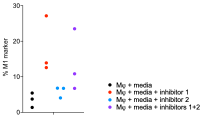
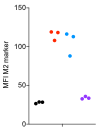
Expression of M2 and M1 marker) by macrophages can be result of downstream signalling of receptors:
Problem:
To test the effect of a modified macrophage medium in inducing the differentiation of anti-tumour macrophages in cancer therapy.
Approach: in vitro macrophage polarisation assay
A modified macrophage M2-type polarising medium with varied growth factors designed to facilitate specific M2-inhibitors used in cancer therapy was tested in a human M2 polarisation model to test if the modified condition was better suited for the inhibitors targeting M2-differentiation.
Findings:
The known inhibitors were effective individually, but when combined there was no effect. The density (%) and intensity (expression) of M2-markers were contrasting. These are due to events in downstream intracellular signalling.
Signal transduction studies are needed to better explain such complex but consistent readouts.