Case Study:
Immuno-Oncology & immuno-Toxicity.
What was the challenge?
Immuno oncology is a fast growing area in drug discovery. The immune system is seriously involved with tumours and cancer through macrophages, NK cells, T cells and dendritic cells. These cells and several immune checkpoints are major targets for intervention or cancer diagnosis. One of the issues in modulating conditions for immune cells for cancer treatment is that above certain threshold conditions may become cytotoxic for immune cells, giving rise to immunotoxicity. Research in immune oncology is coupled with immunotoxicity.
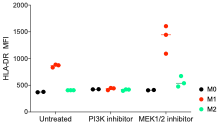
Effect of PI3K inhibition (LY294002) and MEK1/2 inhibition (trametinib) on polarisation of M1 macrophages:
HLA-DR expression
Effect of PI3K inhibition (LY294002) and MEK1/2 inhibition (trametinib) on viability of macrophages:
Trametinib induces immunotoxicity of M1 cells
Problem:
To test the effect of an anti-cancer drug on M1 macrophage polarization and macrophage viability.
Approach:
Macrophage polarisation is a target pathway in immuno oncology and promoting the inflammatory M1 type is a popular route. We tested a known anti-cancer drug Trametinib, an inhibitor of MEK1 and MEK2 in an in-house cell-line based macrophage polarisation model in its ability to promote the inflammatory M1 type macrophage and effect on cell viability. An inhibitor of PI3K, LY294002 was also used as a control.
Findings:
- Trametinib significantly increased the M1 profile of macrophages but also affected cell viability
- LY294002 showed the opposite effects of trametinib
Added value:
Data on cell signaling pathway