Case Study:
Immune Modelling & Experimental Design.
What was the challenge?
Studies in experimental immunology commonly involve complex immune pathways that cannot be tested by single or standard assays. The designing of the experiment in a model is necessary with the consideration and knowledge of multiple factors in the signalling cascade, the interaction of multiple cells and their immunogenic or tolerogenic response.
Problem:
Assess if danger signals can affect the initiation of an autoimmune response.
Approach:
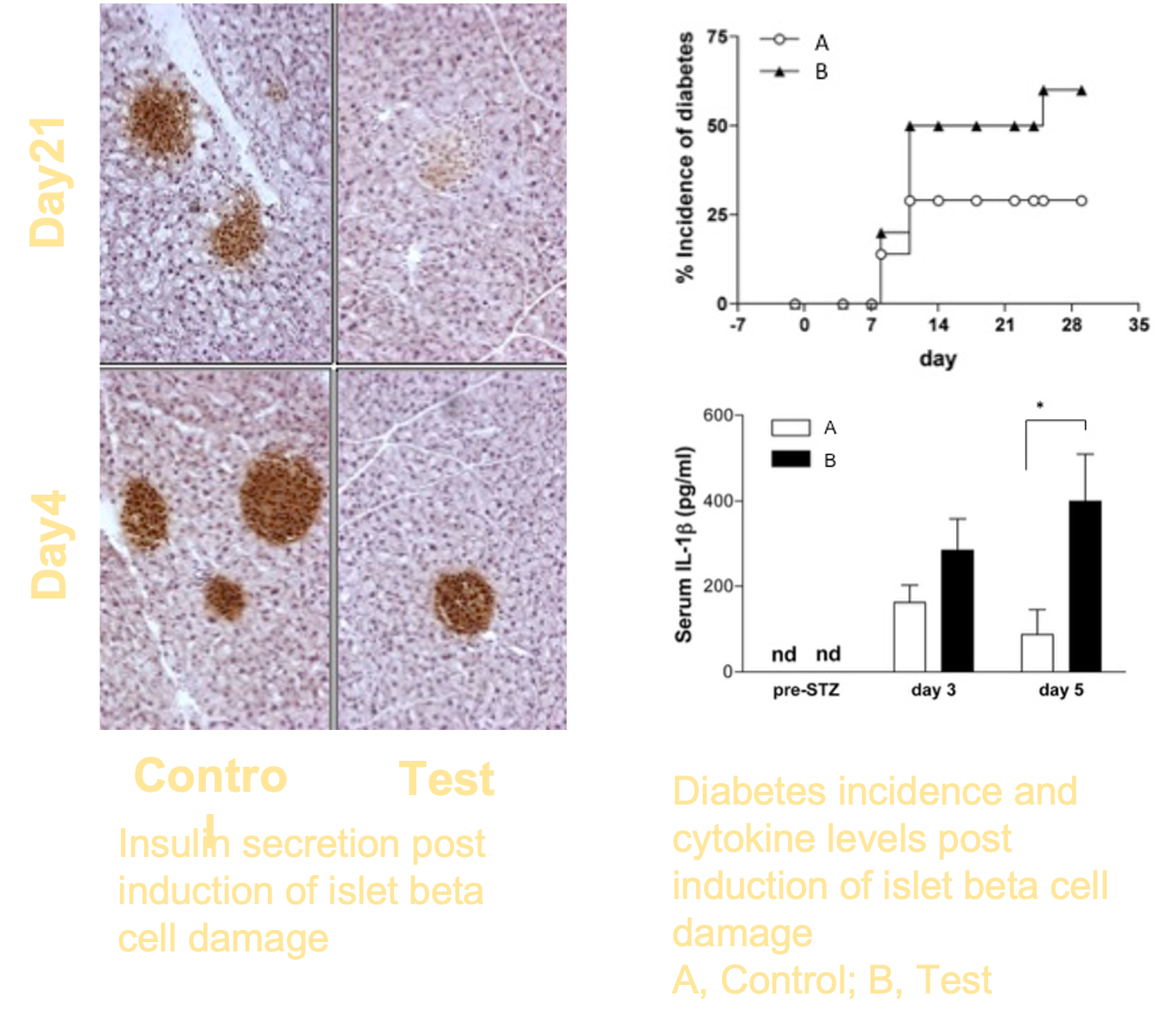
HSC70, a chaperone was chosen as a constitutively expressed protein that acts as a danger signal. An engineered in vivo model was designed with the over expression of HSC70 in beta islet cells only, and Ag-specific CD8+ T cells. In a sterile inflammation, diabetes was induced with targetted islet beta cell damage. Incidence of diabetes was measured, and DC and T cell responses were determined to assess immune tolerance versus immune activation leading to autoimmunity.
Findings:
- Initial beta cell death was responsible for the initiation of an immune mediated diabetes
- The immune response was increased by the over-expression of danger signal
Added Value:
- This model can be adapted into human cell based modules for translational data,
- Intervention points for treatments can be tested,
- Mechanistic data on signaling pathways for drug targeting can be generated.